Worms - what are they?
As we said above, adult worms traditionally have stable positioning within the body, their developmental forms often migrate to different organs and tissues, and their movement paths are often quite complex. For example, with ascariasis, a person becomes infected by eating food contaminated with roundworm eggs (the roundworm eggs mature underground).
What is helminthiasis (helminthiasis) - symptoms of helminths
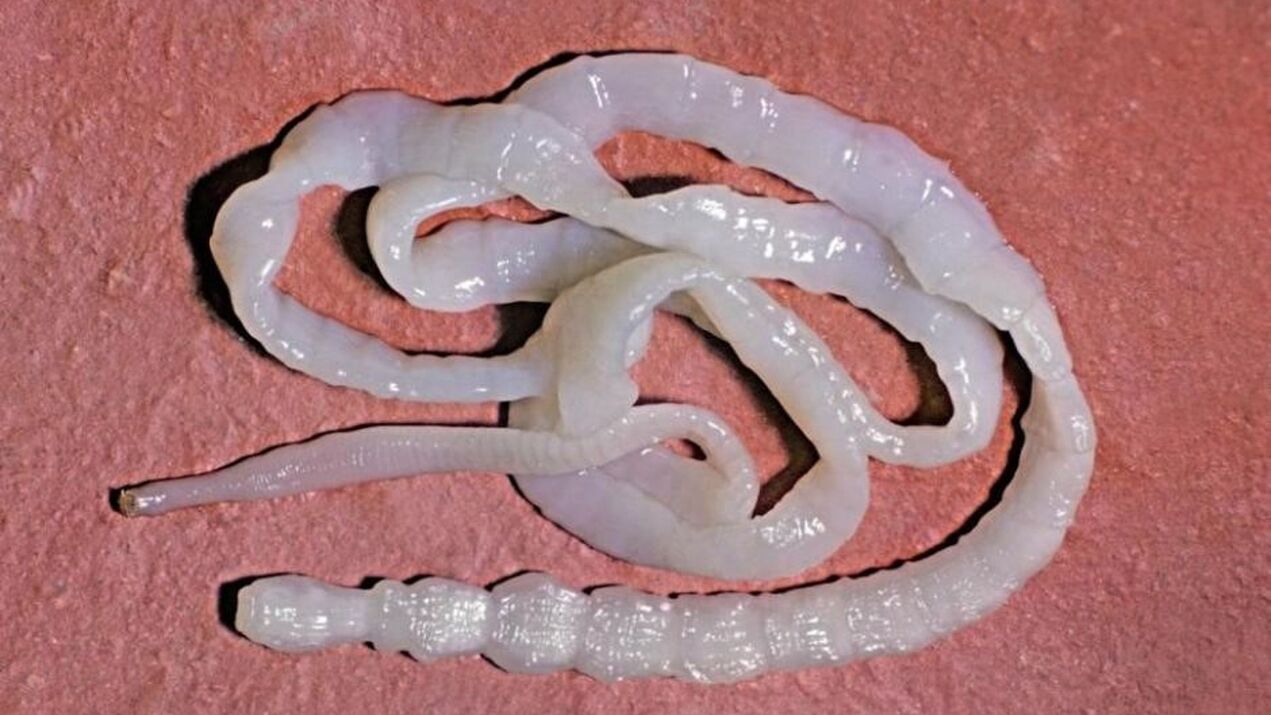

what are these?
- Pinworms are small worms found in the human body that can grow up to 12 mm in length. This type of worm is diagnosed in the intestinal mucosa. Parasites enter the body through the respiratory tract along with dust and are easily spread from person to person.
- Roundworms are large roundworms most commonly found in the small intestine. Infections in the body occur through unwashed hands and food. More commonly, roundworms are found in children.
- Trichinella spiralis - These parasites have round bodies, no more than 5 mm in length, and can cause trichinellosis in the body. Larvae and eggs prefer poorly fried meat (boar, pork, bear). In the human body, Trichinella spiralis takes up to 4 days to become an adult and has a life cycle of 40 days. The main goal of this worm is to enter the bloodstream through the intestinal wall and settle in the muscles. In addition, muscles of the respiratory and musculoskeletal systems are often affected.
- Pork/cattle tapeworm. The parasite is 5-6 meters long and its larvae are hidden in the meat of large animals (pork, cattle). The diseases caused by these worms are called taeniasis and taeniasis. The larvae of both tapeworm species are white vesicles that attach to the walls of the small intestine. It takes 3 months for the parasite to reach and form an adult, and the worms are developing every day. There are 2, 000 segments in total, with the last segment free to "furrow" in the large intestine. The worms then leave the body through the anus along with the feces. The most common and obvious symptoms of helminthiasis are damage to the digestive tract and heavy eating, without significant weight gain.
- Nematodes/hookworms. The link between these parasites is direct due to the diseases they cause and their biological properties. They live in the duodenum and due to their small size (10-15 mm) they can move freely in the environment. The larvae can only enter the body through the skin if a person has come into contact with contaminated soil. Further targets of the worms are the lungs and digestive tract. They feed only on the blood flowing from the blood vessels that have been bitten. Due to the vigorous activity of these parasites, blood coagulation is disrupted. Adults consume blood in the range of 0. 1-0. 35 ml per day.
- Echinococcus tapeworm. In this case, humans serve as intermediate hosts, as the final hosts are wolves, cats, and dogs. Animals may become infected through direct contact with contaminated objects or people. As soon as the parasite eggs enter the intestine, they immediately develop into larvae with six hooks, which are medically called "oncospheres. "
- Whipworm is diagnosed in a person's stomach. These are thin and large worms.
How common and dangerous are worms?
Where do worms spread in humans?
- All types of tapeworms, whipworms, and nematodes "settle" in the large intestine;
- Flukes attack the liver and gallbladder;
- Pork tapeworm larvae can spread through the bloodstream to all organs - subcutaneous fat tissue, eye chambers and blood vessels in the muscles may all be affected.
How do you get infected with worms?
through soil
from one person to another
through water
Symptoms of worms
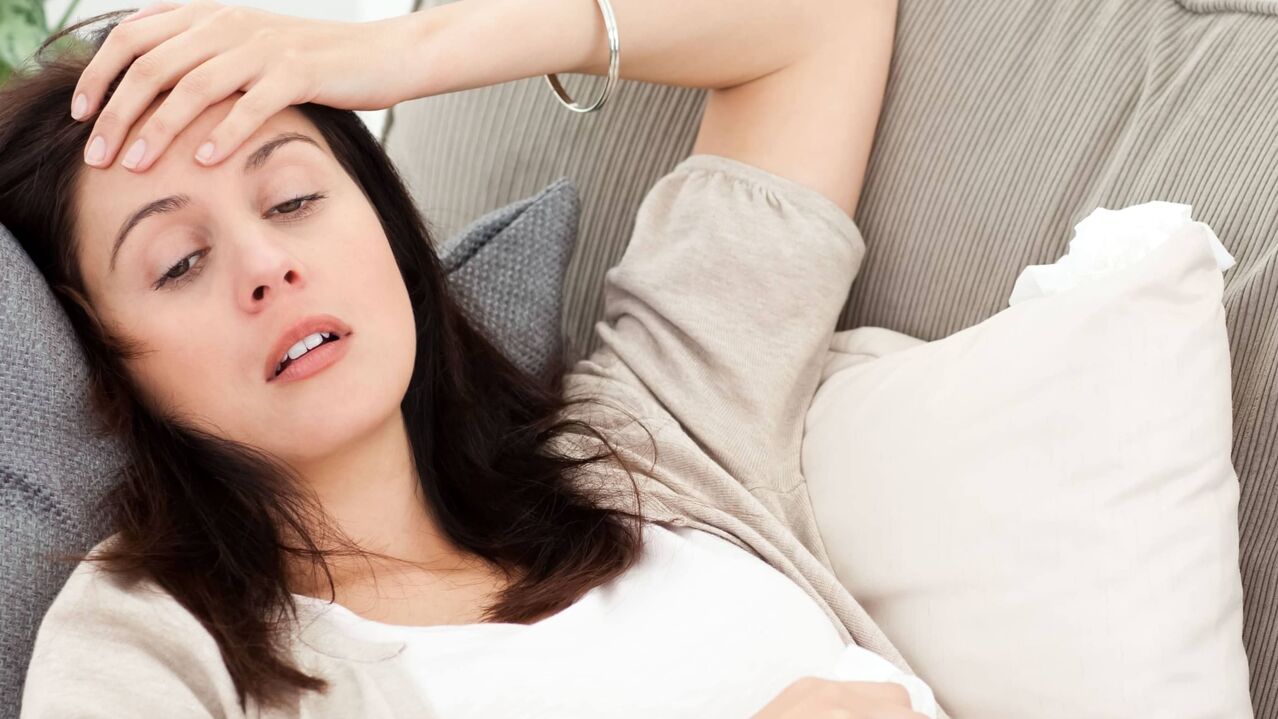

Trichocephaly is hemorrhagic (with bleeding) colitis. Suffering from hookworm disease - iron deficiency anemia. With ascariasis, mechanical obstruction of the intestines and bile ducts may occur. When helminthiasis is accompanied by liver damage, chronic hepatitis and inflammation of the biliary tract (cholecystitis, cholangitis) may occur.
Diagnosis of worms. worm treatment